Hailo¶
CVEDIA-RT supports Hailo H8, Hailo H15, Hailo H10 and all its variants in either M.2, PCI-E and standalone versions.
Limitations
Some models are not available in this platform, when this happens CVEDIA-RT will automatically fallback to the next best backend.
Supported Hailo versions¶
| HailoRT | DFC | CVEDIA-RT Version | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.13.0 | 3.23.0 | 2023.4.x | |
| 4.14.x | 3.24.0 | 2023.5.x | |
| 4.16.0 | 3.26.0 | 2024.1.x | |
| 4.17.0 | 3.27.0 | 2024.2.0 | |
| 4.17.0 | 3.27.0 | 2024.2.1 | |
| 4.16.0 | 3.26.0 | 2024.2.2 | |
| 4.16.0 | 3.26.0 | 2024.2.3 | |
| 4.16.0 | 3.26.0 | 2024.2.4 | |
| 4.16.0 | 3.26.0 | 2024.2.5 | |
| 4.16.0 | 3.26.0 | 2025.1.0 | |
| 4.23.0 / 5.1.0 | 3.33.0 | 2026.1.0 |
HailoRT Versions
The version of HailoRT must match the table above for acceleration to work; As of HailoRT 4.23, there's a different driver for H8 and H15/H10.
Supported Hailo Hardware arch¶
- HailoH8
- HailoH8L
- HailoH8R
- Hailo15M (HailoRT 4.16+)
- Hailo15H (HailoRT 4.16+)
- Hailo10H (HailoRT 4.19+)
HailoRT driver¶
If the installed driver and CVEDIA-RT supported driver don't align models won't be able to load or might crash the accelerator. Make sure that you have the correct driver installed.
Open Device Manager -> System Devices -> Hailo XX AI -> Properties, you should see the driver version in the General tab:
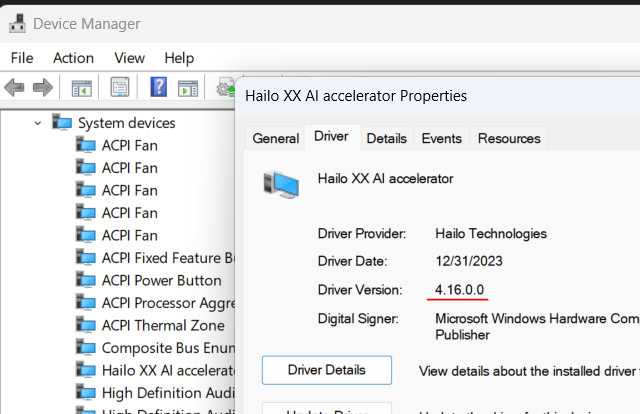
Run ldconfig -v | grep hailo to find what hailort version you've currently loaded.
If you need to install a different driver version on linux...
- Use
apt-getto uninstall hailort - Reboot
- Check if the hailo drivers are gone using
ldconfig -vp | grep hailo, if you still see them delete the related files - Install the proper package
- Reboot
- Check if hailo drivers are loaded and have the correct version with
ldconfig -vp | grep hailo
PCI-E link width¶
It's very important to assure that hailo is running at PCI-E 4x link width. There's a significant loss of performance if you run at 2x or 1x.
To make sure you're running at maximum speed:
You can check on Device Manager -> System devices -> Hailo XX Accelerator -> Details -> PCI current link width
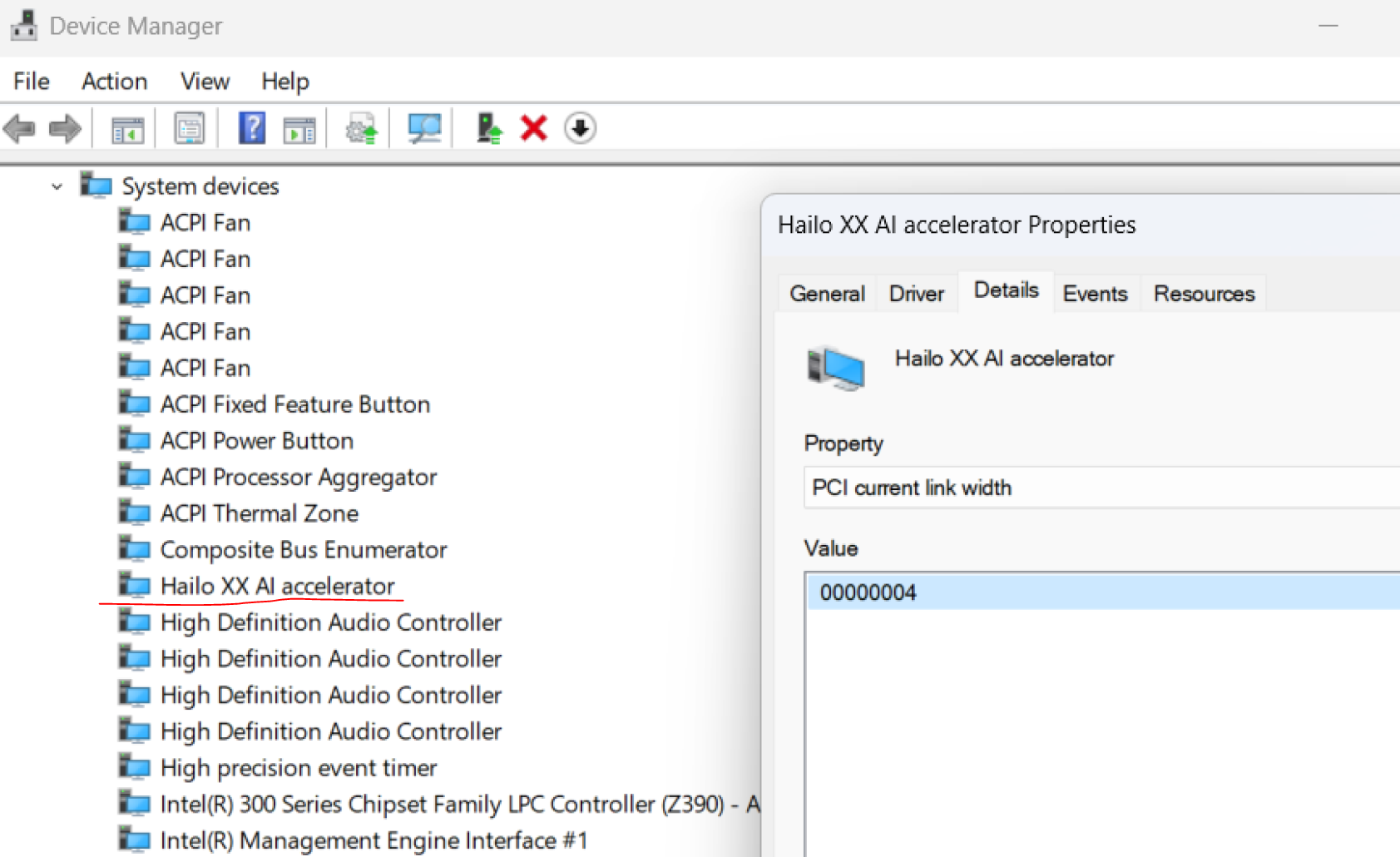
You should see 0000004 , meaning 4x.
Find PCI address of hailo:
# lspci | grep -i co-proc
0000:01:00.0 Co-processor: Device 1e60:2864 (rev 01)
Query For speed:
# lspci -vv -s 0000:01:00.0 | grep -i width
LnkCap: Port #0, Speed 8GT/s, Width x4, ASPM L0s L1, Exit Latency L0s <1us, L1 <2us
LnkSta: Speed 8GT/s (ok), Width x4
In this case LnkSta is the link established with the device with Speed 8GT/s and Width x4 meaning it's working at full speed. If it says downgraded it means it's working at slower than LnkCap (link capabilities).
Benchmarking Hailo¶
Besides CVEDIA-RT's own benchmarking tools, hailo has a special tool for monitoring the device within their hailortcli bundle.
You can monitor the device by setting HAILO_MONITOR=1 env variable, running RT then opening the monitor using haiortcli monitor.
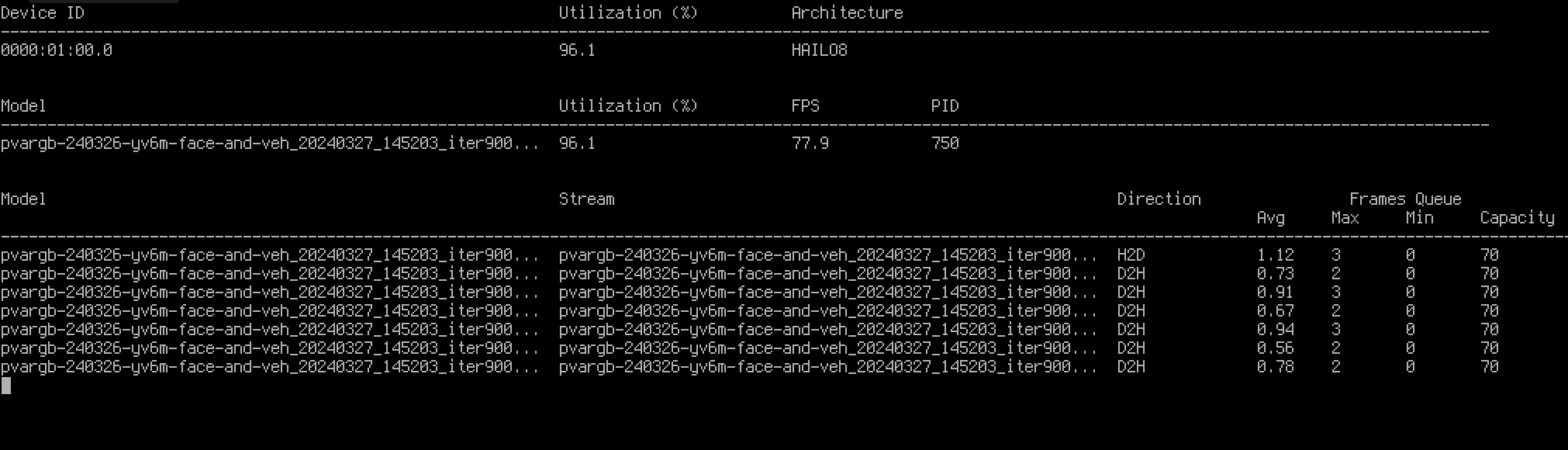
For example on linux native installs, we can run CVEDIA-RT's benchmark tool in the background then run hailortcli monitor to see device utilization:
export HAILO_MONITOR=1
rtcmd inference benchmark -u hailo.auto://pva_det/rgb/medium_y6_mosaic_rot90_320x320/240326 -n 10000 -i 1 -t 16 -p 16 &> /dev/null &
hailortcli monitor
Will show:
How to monitor when running RT inside docker
- Call
./run.shwith-- -e HAILO_MONITOR=1to add the ENV variable globally to the docker container - Shell into the container, eg:
docker exec -it cvedia-rt /bin/bash(the container name might be different) - Install the same version of the release HailoRT within the container
- Run
hailortcli monitorinside the container while RT is using the hardware